The U.S. IRS tax code is a complex web of regulations, forms, and deductions that can baffle even the most seasoned taxpayers. One such form that often confounds individuals and families seeking to maximize their tax benefits is IRS Form 8812, also known as Schedule 8812. This form is specifically designed to help taxpayers claim the Additional Child Tax Credit, a valuable resource for families with children. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore every facet of Schedule 8812, from understanding who needs it to navigating the intricate instructions, all the way to maximizing your tax benefits.
What is Schedule 8812 and Who Needs It?
Before diving into the specifics of IRS Form 8812, let’s start with a brief overview. Schedule 8812 is a supplementary form that taxpayers attach to their IRS Form 1040 when they want to claim the Additional Child Tax Credit. Unlike the regular Child Tax Credit, which is non-refundable, the Extra child tax benefit
is returnable, meaning that if it reduces your tax liability to zero and there is still credit left, you can receive the remaining amount as a refund. This profit from IRs may be a significant financial boon for eligible families.
Criteria for Taxpayers Who Should Consider Credit Using IRS Form
Not every taxpayer needs to use IRS Schedule 8812. The decision to use this tax form depends on your unique tax situation. It’s important to carefully assess your circumstances to determine if filing Schedule 8812 is beneficial for you. Here are the key criteria that indicate you should consider using this form:
1. You Have One or More Qualifying Children
The primary prerequisite for using Schedule 8812 is having one or more qualifying children. Entitled offspring are typically your child and dependent children who meet specific IRS criteria. These criteria include age, relationship, residence, and other factors. If you have one or more children who meet these requirements, Schedule 8812 may be relevant to your tax return.
2. You Are Eligible for the Child Tax Credit but Cannot Claim the Full Amount
The Child Tax Credit is a valuable tax profit that can significantly reduce your tax liability. However, there are income limitations that may prevent you from claiming the full amount of this credit. If you find that your income exceeds the threshold for the full Child Tax Credit, you should explore the Additional Child Tax Credit, which is claimed using Schedule 8812. This credit can provide additional relief for families who do not qualify for the full tax due to income constraints.
3. Your Earned Income Exceeds a Certain Threshold
To be eligible for the Additional Child Tax Credit, you must have earned income. Earned income includes wages, salaries, and self-employment tax income. However, there is a minimum threshold of earned income required to claim this credit. If your earned income surpasses this threshold, you may qualify for the Supplementary child tax rebate. This credit is designed to assist families with working parents, and if you fall within this category, Schedule 8812 can help you maximize your tax benefits.
Explaining the Concept and Purpose of the Additional Child Tax Credit
The Additional Child Tax Credit is designed to provide additional financial assistance to families with children. It recognizes that raising children can be costly, and it aims to ease the financial burden by providing a credit that is refundable, meaning you can receive it even if you don’t owe any taxes. This is a crucial distinction from the regular Child Tax Credit, which can only reduce your tax liability but not result in a reimbursement.
How It Differs from the Regular Child Tax Credit
It’s essential to understand the difference between the regular Child Tax Credit and the Additional Child Tax Credit:
- Regular Child Tax Credit: This credit is non-returnable and can only reduce your tax liability to zero. If you don’t owe any taxes, you won’t receive any money from it.
- Supplementary child tax rebate: This credit is reimbursable. If it reduces your tax liability to zero and there’s still a remaining credit amount, you can get that amount as a return. This can be a significant financial benefit for many families.
Now that we’ve covered the basics of the Additional Child Tax Credit, let’s move on to the eligibility criteria for this credit.
Who Qualify for the Child Tax: Tax Prep?
To claim the Additional Child Tax allowances, you must have one or more qualifying dependent. A qualified minors typically must meet the following criteria:
-
- Be under the age of 17 at the end of the tax year.
- Be a U.S. citizen, U.S. national, or U.S. resident alien.
- Be your son, daughter, stepchild, foster child, brother, sister, stepbrother, stepsister, or a descendant of any of them.
- Have lived with you for more than half of the fiscal year.
- Not provide more than half of their own support for the tax year.
- Have a valid Social Security Number.
Income Thresholds and Other Requirements to Claim the Credit
Eligibility for the Additional Child Tax Credit is also determined by your income. The credit begins to phase out if your modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) exceeds certain thresholds. Understanding these income limits is crucial when determining your eligibility.
The income thresholds for the Additional Child Tax Credit vary depending on your filing status. For the tax year 2022, the thresholds are as follows:
| Filing Status | Phase-Out Threshold (MAGI) |
|---|---|
| Married Filing Jointly | $400,000 |
| Head of Household | $200,000 |
| Single or Qualifying Widow/Widower | $200,000 |
| Married Filing Separately | $200,000 |
It’s important to note that these thresholds are subject to change due to inflation and adjustments made by the IRS each tax year.
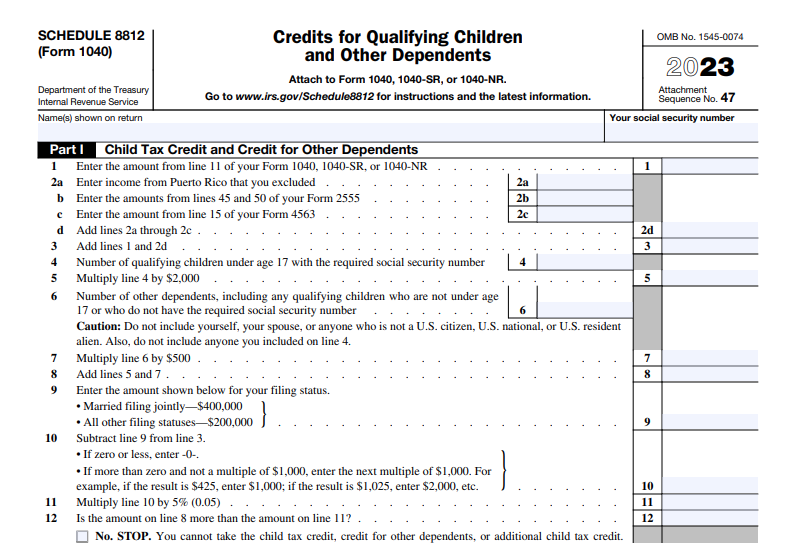
Filling Out Schedule 8812 Instructions
Filling out Schedule 8812 may seem daunting at first glance, but with a step-by-step guide, you can navigate it with confidence. Here’s a breakdown of how to complete Schedule 8812 with filing instructions to get tax relief:
- Part I – Child Information: In this section, you’ll provide the necessary information about your qualifying dependent or children, including their names, SSN, and relationship to you.
- Part II – Here, you’ll calculate your credit amount you’re eligible for. This involves entering various figures, including the Child Tax rebates from Form 1040 and your earned income.
- Part III – Refundable Portion: This part helps you determine the reimbursable portion of the credit. It involves comparing your tax liability to the total credit amount.
- Part IV – Nonrefundable Portion: In this section, you’ll calculate the nonrefundable portion of the credit, which is limited to 15% of your earned income over $2,500.
Common Errors to Avoid During Completing Schedule 8812
When dealing with IRS Form 8812 and the Additional Childs Tax Credit, it’s imperative to be vigilant and avoid common errors that can have adverse effects on your tax return. These errors can lead to delays in processing your return or result in incorrect credit amounts. To help you steer clear of these pitfalls, here are some of the most prevalent mistakes to watch out for:
- Inaccurate Information About Your Qualifying Child: Providing precise and up-to-date information about your qualifying child is paramount. Ensure that you enter their correct Social Security Number (SSN) or Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN). Mistakes in these numbers can lead to disqualification for the credit or delays in processing.
- Incorrect Credit Amount Calculations: The calculation of the credit amount can be a complex task. Errors in arithmetic or misunderstanding the IRS guidelines can result in inaccurate credit amounts. It’s essential to carefully follow the instructions on Form 8812 and double-check your calculations.
- Failure to Understand Refundable and Nonrefundable Portions: The Additional Child Tax Credit consists of both reimbursable and nonrefundable portions. Understanding how these components work is crucial. The returnable portion can lead to a tax refund even if you don’t owe any taxes, while the nonrefundable portion can only reduce your tax liability. Failing to differentiate between the two can lead to missed opportunities for a refund.
- Neglecting Life Events Affecting Eligibility: Life events such as divorce, remarriage, or changes in custody arrangements can significantly impact your eligibility for the Additional Child Tax Credit. Failure to consider these changes in circumstances can result in erroneous claims or denials.
To avoid these common errors and ensure a smooth filing process, it’s essential to meticulously follow the instructions provided on Form 8812. Additionally, employing tax software or seeking guidance from a tax professional can be valuable in minimizing the risk of errors and maximizing your tax profits.
Tax Credits vs. Tax Deductions: Understanding the Impact on Your Income Tax Return
Before we proceed, it’s essential to clarify the difference between tax credits and tax deductions:
| Category | Description | Effect on Taxes |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Credits | Tax credits directly reduce the amount of taxes you owe. | For example, if you owe $5,000 in taxes and are eligible for a $2,000 tax credit, your tax liability is reduced to $3,000. |
| Tax Deductions | Tax deductions reduce your taxable income. They do not directly reduce the taxes you owe but lower the income that is subject to taxation. | For example, if you have a $10,000 deduction and your taxable income is $50,000, you’ll only pay taxes on $40,000. |
Specifics of How Tax Credits Like Schedule 8812 Impact Your Tax Bill
Now that we understand the fundamental difference between tax credits and deductions, let’s delve deeper into how tax credits like Schedule 8812 can impact your tax invoice, as outlined in federal tax law and IRS regulations.
- Tax credits like Schedule 8812, which are detailed in the instructions for Form 8812, are extremely valuable because they directly reduce the taxes you owe, dollar for dollar. This is particularly true for the Additional Child Tax Credit on form 8812. This tax credit reduces your federal earnings tax filing liability and can lead to a significant credit amount. In some cases, if the credit amount exceeds the amount of tax owed, it can even result in a refund, making it a crucial component of individual earnings tax considerations.
- To claim a child under Schedule 8812, the child meets specific criteria set forth by the IRS. The total credit amount you can receive is determined per child and is subject to the limitations of your adjusted gross income. This means that if your tax liability is less than the credit, you may still receive a credit due to you, potentially exceeding the amount you owe.
- Tax credits can significantly lower your overall tax burden, especially if you have a low tax liability to begin with. This makes them a powerful tool for taxpayers, particularly those who need to file a federal revenue tax return with considerations such as self-employment tax. Schedule 8812 requires careful attention to compute your credit value
accurately. - Unlike deductions, which depend on your tax bracket, tax credits provide the same financial benefit regardless of your income level. Therefore, when you file your tax return, it’s important to understand the IRS publication and IRS regulations that guide these credits. You need to complete the appropriate forms and follow the specific tax prep instructions to ensure you maximize your credit due.
- For taxpayers with self-employment income, the impact of Schedule 8812 on their tax bill can be significant. While calculating your credit amount, it’s important to consider how this credit interacts with your self-employment tax and total income after modifications. According to federal tax law, these factors play a crucial role in determining your final tax liability.
Maximizing Your Child Tax Credits
Strategies to Fully Utilize the Child Tax Credit and Additional Child Tax Credit
To maximize your Child Tax rebates and Additional Child Tax Credit, consider the following strategies:
- Understand the Rules: Familiarize yourself with the Internal Revenue Service rules and eligibility criteria to ensure you qualify for the maximum credit amount.
- Plan Your Income: If your income is close to the phase-out threshold, consider strategies to lower your MAGI, such as contributing to retirement accounts.
- Update Your Information: Make sure all your information, including your child’s Social Security Number, is up-to-date and accurate to avoid processing delays.
- Use Tax Software or a Tax Professional: Tax software and professionals can help you navigate the complexities of the tax code, ensuring you claim all eligible credits.
Role of Tax Software and Professionals in Optimizing Credits
Tax software and professionals play a vital role in optimizing your child tax credits:
- Tax Software: Using tax software simplifies the process of claiming credits like Schedule 8812. It guides you through the necessary steps, performs calculations, and helps you avoid common errors.
- Tax Professionals: Enlisting the help of a tax expert ensures that you receive expert advice tailored to your specific financial situation. They can identify additional tax-saving opportunities and provide peace of mind that your return is accurate and compliant with tax laws.
Recent Changes in Tax Laws Affecting Child Tax Credits
Tax laws are subject to change, and staying informed about recent developments is crucial when claiming child tax credits. Some recent changes that may impact your tax return include:
- American Rescue Plan Act: This legislation temporarily increased the Child Tax Credit for the tax year 2021. It provided advance payments to eligible families.
- Tax Cuts and Jobs Act: This tax reform legislation made significant changes to the Child Tax rebates, increasing the maximum credit amount and altering income thresholds.
- Future Legislation: Tax laws can change with each new congressional session, so it’s essential to stay updated on any relevant changes that may affect your tax situation.
Implications for Taxpayers Filing Schedule 8812
The implications of tax law changes for taxpayers complete Schedule 8812 form can be substantial. Changes in credit amounts, income thresholds, and eligibility criteria can affect the amount of credit you’re eligible to claim. To ensure you’re taking advantage of the latest tax laws, consult tax advisor or stay informed about IRS updates.
Benefits of Using Tax Software for Filing child tax credit on form
Tax software offers numerous benefits when it comes to complete Schedule 8812 form and claiming child tax concessions:
- Accuracy: Tax software helps eliminate errors in calculations and data entry, reducing the risk of processing delays or Internal Revenue Service inquiries.
- Guided Process: Software guides you through each step of filling out Schedule 8812, ensuring you don’t miss any important details.
- Efficiency: Using software can significantly speed up the filing process, allowing you to submit your return quickly and accurately.
- E-filing: Most tax software allows for e-filing, which can expedite the processing of your return and provide faster access to any refunds.
How Tax Software Simplifies the Process of Claiming Credits
Tax software simplifies the process of claiming credits like Schedule 8812 in the following ways:
- Automated Calculations: The software performs all necessary calculations, such as determining the returnable and nonrefundable portions of the credit, ensuring accuracy.
- Error Checks: Software checks for common errors and prompts you to correct them, reducing the likelihood of mistakes.
- Updated Forms: The software provides access to the latest IRS forms, including Schedule 8812, ensuring you’re using the most current version.
Common Questions About Form 8812 Instructions
Addressing Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Schedule 8812
Here are answers to some common questions about Schedule 8812:
1. Do I Need to File Schedule 8812 Separately?
No, Schedule 8812 should be attached to your Form 1040 when you’re filing your federal income tax return. It’s not filed separately.
2. Can I Claim the Child Tax Credit and the Additional Child Tax Reductions?
Yes, you can claim both the Child Tax concessions and the Extra child tax benefit if you meet the eligibility criteria for both.
3. What If My Child Was Born or Passed Away During the Year?
If your child was born or passed away during the tax year, you may still be able to claim the Child Tax Credit for that child, depending on the timing of the event. Consult Internal Revenue Service guidelines or a tax specialist for specific guidance.
4. What Happens If My Credit Amount Exceeds My Tax Liability?
If the credit amount calculated on Schedule 8812 exceeds your tax liability, you may be eligible for a refund for the excess amount. This is one of the key benefits of the Additional Child Tax Credit.
5. Can I Claim the Credit for Other Dependents Using Schedule 8812?
No, Schedule 8812 is specifically for claiming the Additional Child Tax reductions. If you have other dependents who don’t meet the criteria for the Child Tax Credit, you may be entitled to assert the Credit for Other Dependents on your Form 1040.
Specific Considerations for Families with More Than One Qualifying Child
Families with multiple qualifying children may have additional considerations when apply for the child tax credit and the Additional Child Tax Credit:
- Calculating Credits: The credit amount is determined separately for each qualifying child, so you’ll need to calculate it for each child individually.
- Increased Benefits: Families with multiple children might qualify for larger total credits, potentially resulting in a more substantial refund.
- Accurate Information: Ensure that you provide accurate and complete information for each qualifying child to avoid processing delays.
Tax Tips for Maximizing Credits for Larger Families
To maximize credits for larger families, consider the following tips:
- Claim All Eligible Children: Make sure you claim the Child Tax Credit for all qualifying children.
- Check Income Thresholds: Be aware of the income thresholds and plan your finances to stay within the eligibility limits.
- Seek Professional Advice: For families with complex tax situations, consulting a tax professional can help you optimize your tax credits.
Final Thoughts on Effectively Utilizing the Additional Child Tax Credit
In our final section, we will emphasize the significance of effectively utilizing the Additional Child Tax reductions and how it can positively impact your financial situation. We will leave you with some parting thoughts and encouragement to make the most of this valuable tax benefit.
By the end of this detailed guide, you will be well-equipped to navigate Internal Revenue Service Form 8812, unlock additional child tax credits, and confidently file your taxes. Whether you have one qualifying child or several, understanding the intricacies of Schedule 8812 can lead to significant tax savings and a more financially secure future.